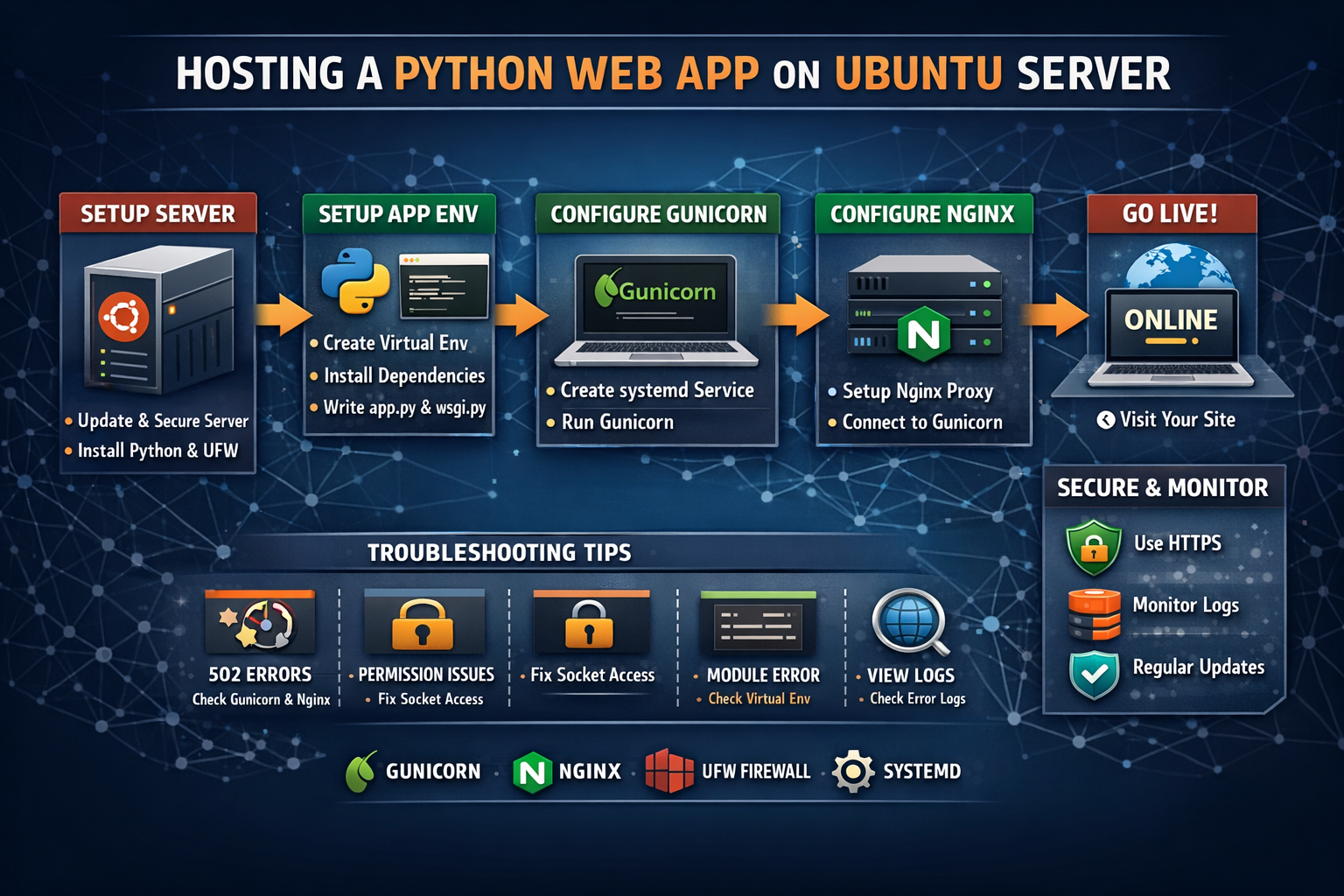
How to Host a Custom Python Web App on Ubuntu Server
Overview of the Stack
We will use:
Ubuntu Server – Operating system
Python 3 – Application runtime
Virtualenv – Dependency isolation
Gunicorn – Python WSGI application server
Nginx – Reverse proxy & static file server
systemd – Service management
UFW – Firewall
This setup is secure, scalable, and production-ready.
1. Initial Server Setup
1.1 Update the System
Always start by updating your server:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Reboot if required:
sudo reboot
1.2 Create a Non-Root User (Recommended)
sudo adduser webuser
sudo usermod -aG sudo webuser
su - webuser
This improves security by avoiding root access.
1.3 Install Required Packages
sudo apt install -y python3 python3-pip python3-venv \
nginx git ufw
Verify versions:
python3 --version
pip3 --version
nginx -v
2. Firewall Configuration (UFW)
Enable firewall and allow essential services:
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'
sudo ufw enable
Check status:
sudo ufw status
3. Prepare Your Python Web Application
3.1 Create Project Directory
mkdir -p ~/apps/myapp
cd ~/apps/myapp
Example structure:
myapp/
│
├── app.py
├── requirements.txt
├── wsgi.py
└── venv/
3.2 Create a Virtual Environment
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Upgrade pip:
pip install --upgrade pip
3.3 Install Application Dependencies
Example for Flask:
pip install flask gunicorn
Save dependencies:
pip freeze > requirements.txt
3.4 Sample Flask App (app.py)
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def home():
return "Hello from Ubuntu Server!"
3.5 WSGI Entry Point (wsgi.py)
from app import app
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run()
Test locally:
gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 wsgi:app
Visit:
http://SERVER_IP:8000
If it works, stop Gunicorn:
CTRL + C
4. Configure Gunicorn as a systemd Service
4.1 Create Service File
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/myapp.service
Paste:
[Unit]
Description=Gunicorn instance for myapp
After=network.target
[Service]
User=webuser
Group=www-data
WorkingDirectory=/home/webuser/apps/myapp
Environment="PATH=/home/webuser/apps/myapp/venv/bin"
ExecStart=/home/webuser/apps/myapp/venv/bin/gunicorn \
--workers 3 \
--bind unix:/home/webuser/apps/myapp/myapp.sock \
wsgi:app
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and exit.
4.2 Start and Enable Service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start myapp
sudo systemctl enable myapp
Check status:
sudo systemctl status myapp
5. Configure Nginx Reverse Proxy
5.1 Create Nginx Site Config
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/myapp
Paste:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your_domain_or_server_ip;
location / {
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://unix:/home/webuser/apps/myapp/myapp.sock;
}
}
5.2 Enable the Site
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/myapp /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Visit:
http://SERVER_IP
Your Python app should now be live 🎉
6. Useful Management Commands
Restart Services
sudo systemctl restart myapp
sudo systemctl restart nginx
View Logs
journalctl -u myapp
sudo tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
Reload Nginx Without Downtime
sudo systemctl reload nginx
7. Common Troubleshooting
Issue: 502 Bad Gateway
Causes:
Gunicorn not running
Socket permissions wrong
Wrong path in Nginx config
Fix:
sudo systemctl status myapp
ls -l ~/apps/myapp/myapp.sock
Ensure group is www-data.
Issue: ModuleNotFoundError
Cause: Wrong virtualenv path or missing dependency
Fix:
source venv/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
Restart service.
Issue: Permission Denied on Socket
sudo chown webuser:www-data myapp.sock
sudo chmod 660 myapp.sock
Issue: App Works with Gunicorn but Not Nginx
Check Nginx error log:
sudo tail -n 50 /var/log/nginx/error.log
8. Security Best Practices
Disable root login via SSH
Use HTTPS (Let’s Encrypt + Certbot)
Use environment variables for secrets
Regularly update the server
Install Certbot:
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx
sudo certbot --nginx
9. Useful Ubuntu Server Commands
htop # Resource usage
df -h # Disk space
free -m # Memory usage
netstat -tulpn # Open ports
ps aux | grep gunicorn
10. Summary
You now have:
A Python web app running in a virtual environment
Gunicorn serving the app
Nginx handling HTTP requests
systemd managing uptime
Firewall protecting your server
This setup is production-ready and scalable for real-world applications.